What are the benefits of Collagen?
Skin. Tendons. Bones. Blood vessels. Gut lining. There isn’t much of the body that doesn’t need collagen. We stop producing it as we age, so supplementation is a must if you want to maintain youthful skin, muscle and support a robust digestive system.
What does the research say?
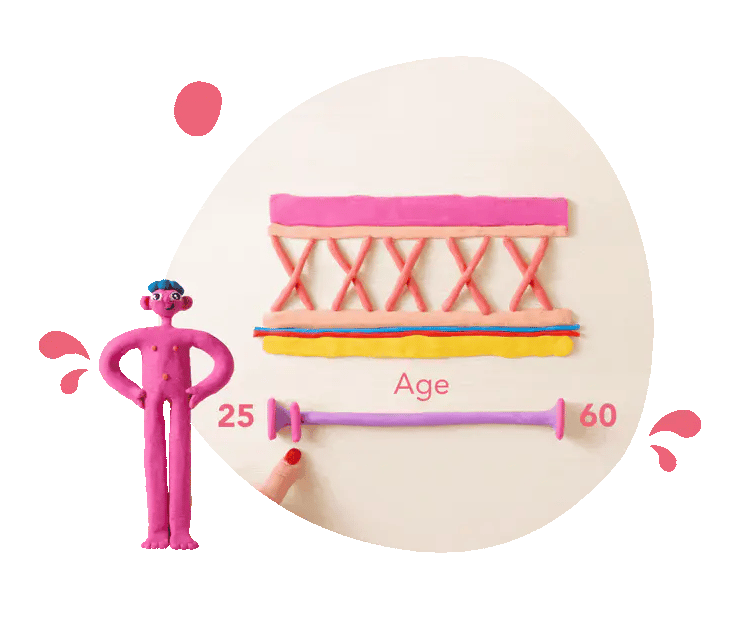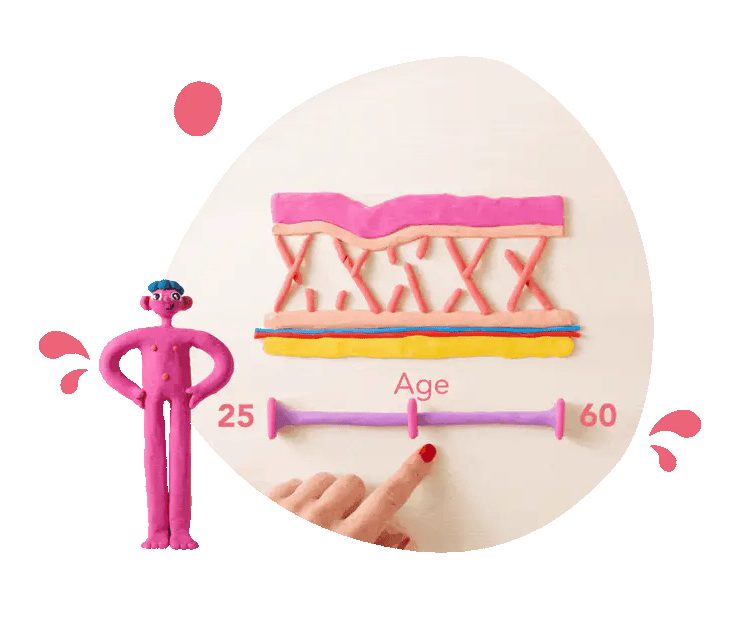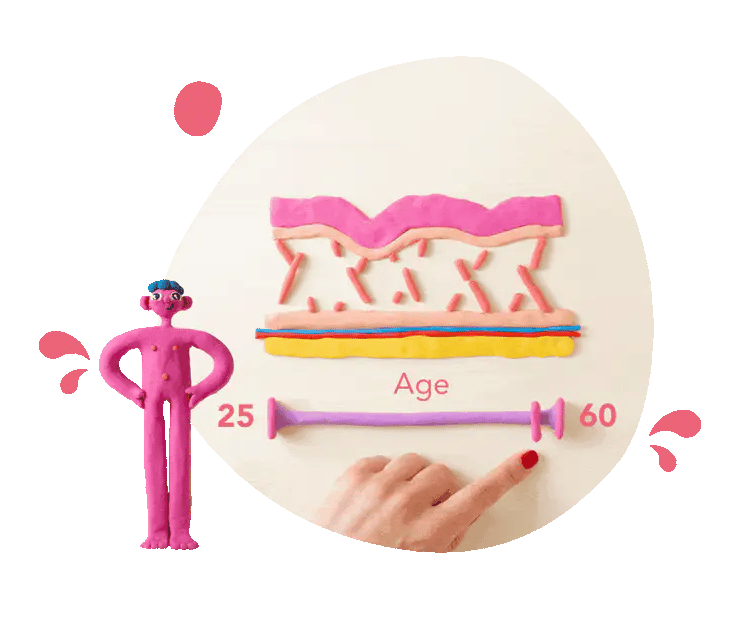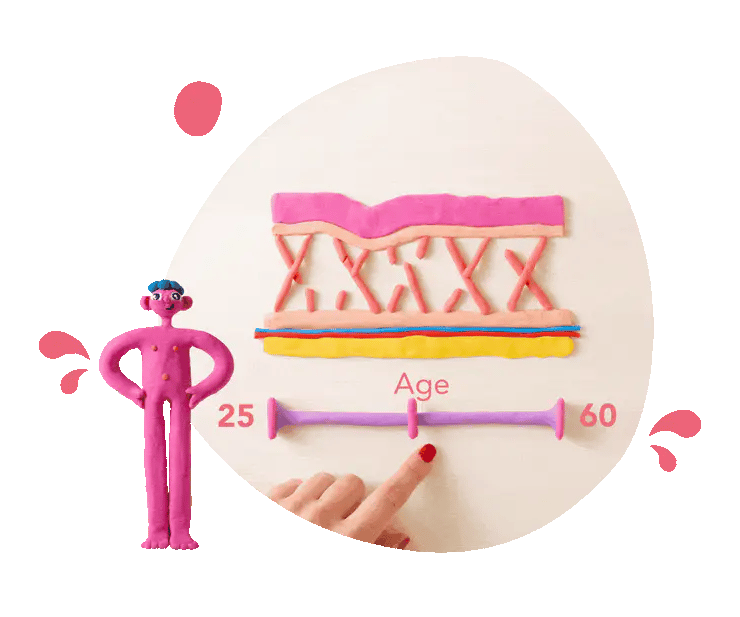
Collagen equals strength
Collagen is the main protein providing the scaffolding and glue for tendons, bones, ligaments and skin. It literally keeps us upright and forms the padding for youthful, robust skin.
As we age, collagen production falls, resulting in weaker tendons and muscles as well as sagging skin and wrinkles. Maintaining collagen levels can support your strength and resilience both inside and outside the body.
How does Collagen work?
Step 1
- Collagen is mostly formed inside cells called fibroblasts, using certain amino acids alongside Vitamin C and zinc.
Step 2
- 3 strands of collagen chains wind tightly together to form a triple helix that is strong and resilient.
Step 3
- The collagen helixes join together to form either sheets or long rope-type fibres that repair, replace and restore connective tissue all over the body,
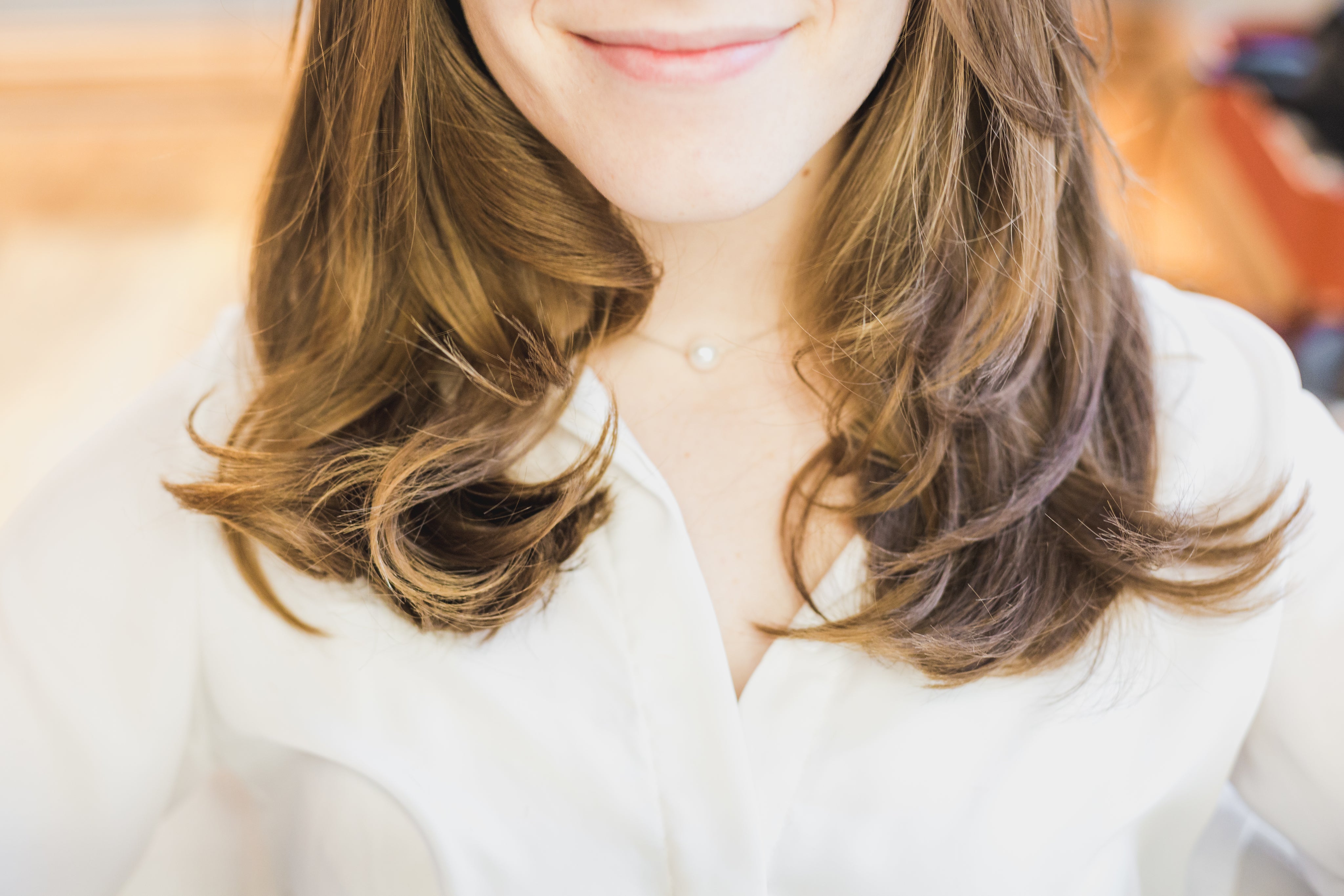

Collagen for skin, hair and nails
Collagen is made up of 3 key amino acids that support the growth and repair of skin, hair and nails. Stable and strong, collagen can slow down the visible signs of ageing through its direct effect on the dermal layer; stimulate hair growth by providing the necessary amino acids and guard against or improve brittle nails from the inside out.
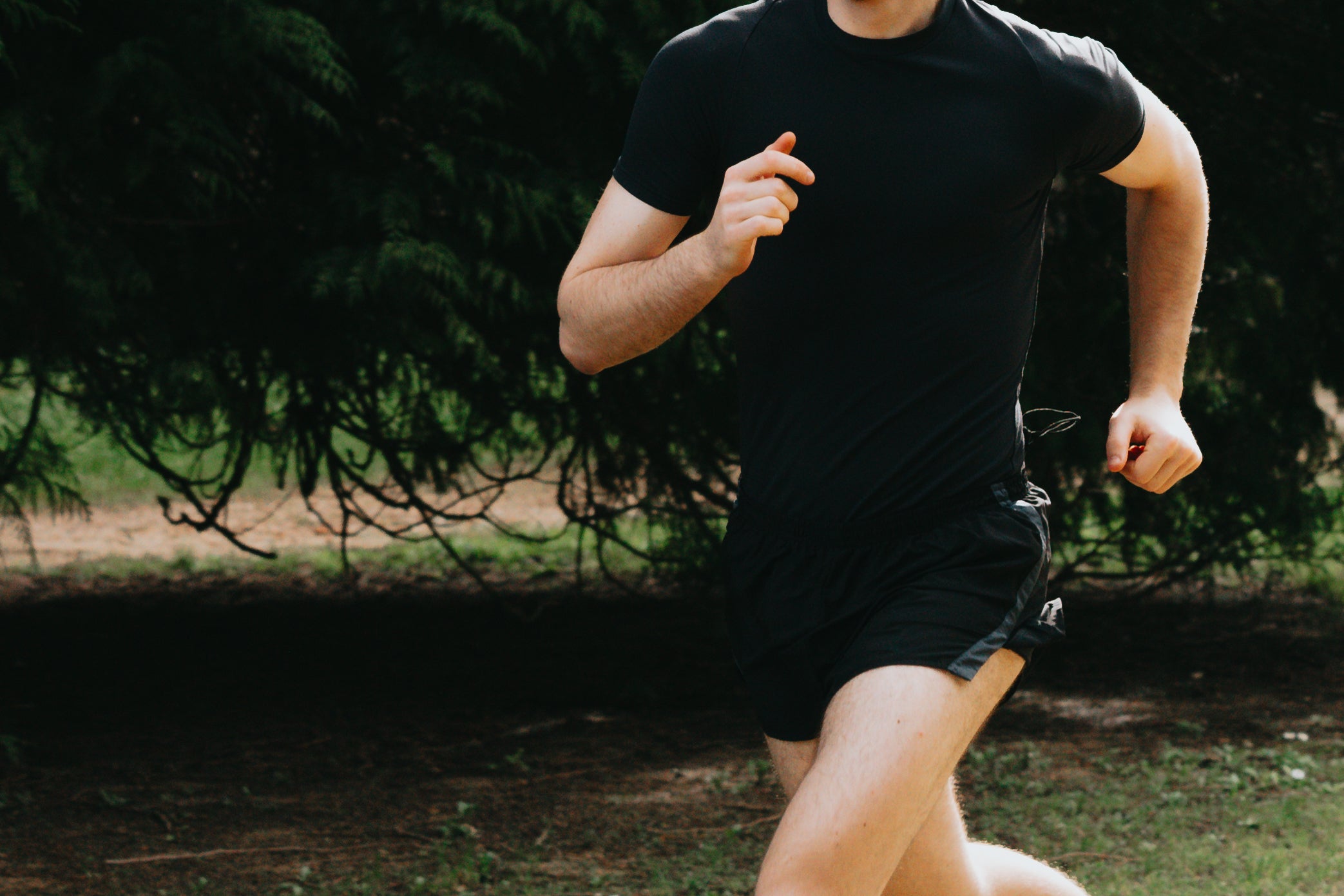

Collagen for athletes
Collagen supports both professional and amateur athletes through its effects on connective tissues, muscle growth and even gut health. Collagen is also important to repair the micro-tears induced during exercise, or more serious injuries when you’ve overtrained. Finally, it’s an important component of bones and the blood vessels that keep the energy pumping!
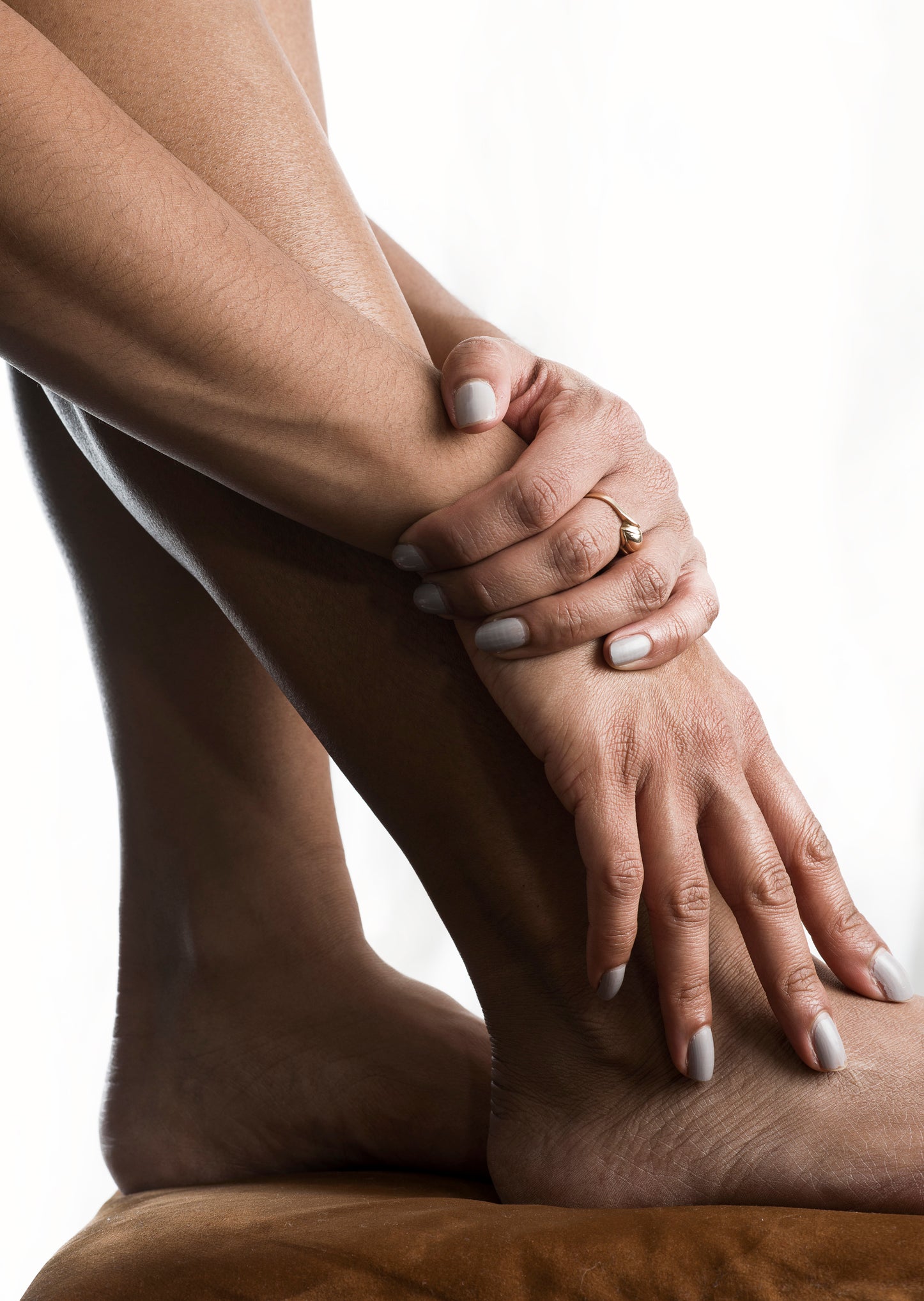

Collagen for joints & bones
Collagen forms a key component of bones and the tissues that connect them. Supplementation can help maintain and may even increase bone density. For the cartilage that surrounds the bones and forms the joints, collagen supplements can aid repair and even stimulate the body’s own natural collagen production.

Collagen for menopause
The loss of collagen production speeds up enormously during menopause, with detrimental effects on skin, muscle and bone strength. But it’s not only collagen that falls during menopause. The collapse of oestrogen levels have knock on effects on tendon, bone and muscle strength. Using collagen can help stabilise those losses and maintain crucial strength.

What is the best way to take Collagen?
Consistency is key if you want to build lasting results. We recommend you take your collagen straight from the fridge on an empty stomach at a time that you will remember daily. Make sure your supplement is broken down (‘hydrolysed’) into small peptides otherwise you won’t absorb it. Taking it with vitamin C also stimulates the body’s own production of both collagen and hyaluronic acid.

Topical vs. ingestible collagen?
Many skin products contain collagen, but absorption through the skin is limited. The body also finds it hard to break down and reformulate the amino acids into collagen that can actually be used. Taking collagen orally ensures better absorption into the bloodstream and that the collagen will be used around the body where it is needed.
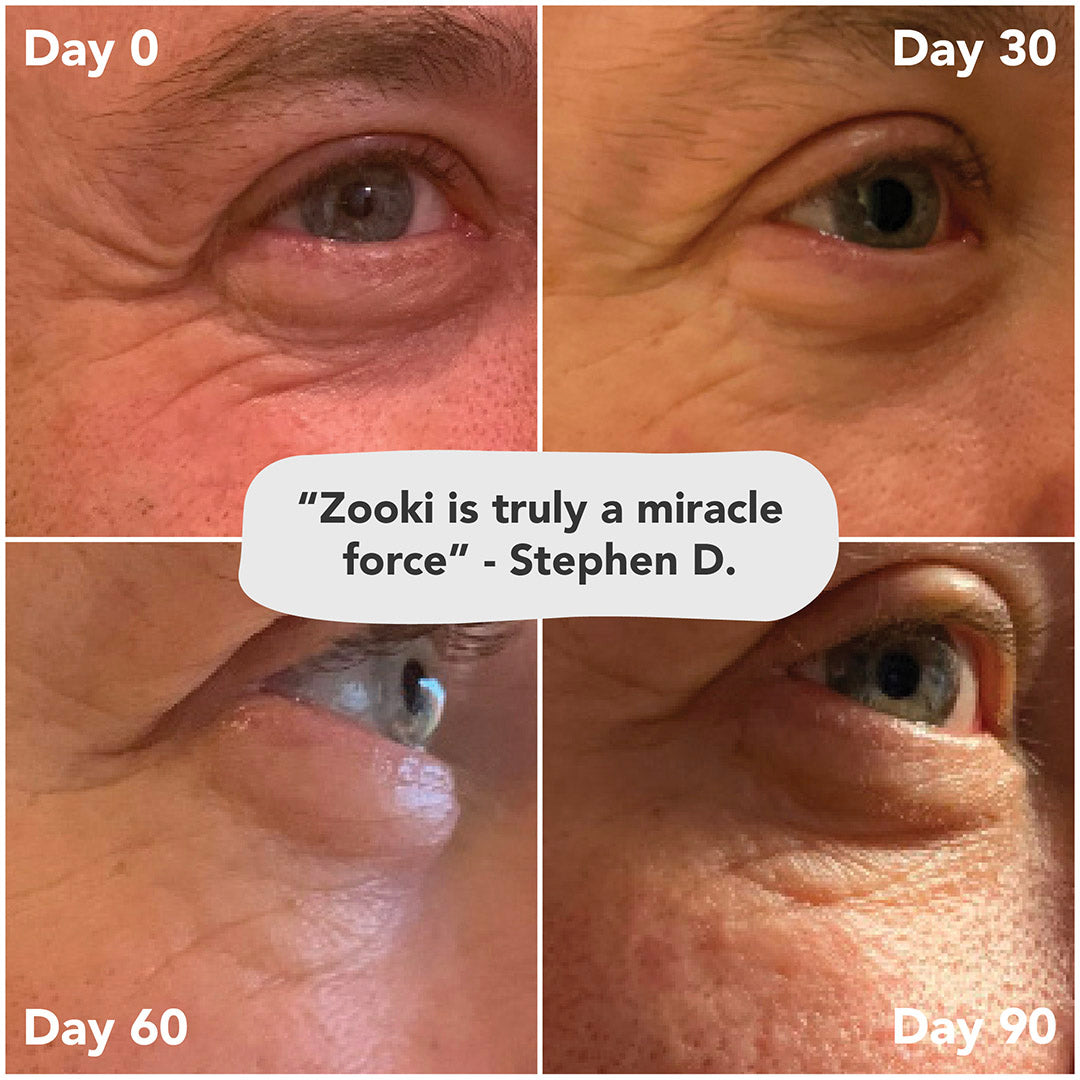
Is Collagen suitable for everyone?
All collagen is derived from animal sources, so it won’t suit vegans. Vegetarians may find eggshell collagen supplements but mostly collagen is made from either fish, beef or pork. Marine collagen is not suitable for anyone with a fish allergy. We normally recommend that people start taking collagen after the age of 25, when the body’s own production slows down. However, if you are working on a gut problem or healing from injury, you can take it younger than that.

How long until I see the effects?
Allow a month for every 10 years of your life. If you’re 30, you should see results after 3 months. If you’re 60, it may take up to 6 months. Taking it consistently is also important as the effects will become more sustainable with regular use.
FAQs
Please read our FAQs page to find out more.
Does collagen interact with any medications?
There are no known interactions between collagen and drugs so far. When used as a supplement it acts in a similar way to protein, so if you are already on a high protein diet, it is worth checking with your doctor as very high levels of protein in the diet can affect the efficiency of certain medications.
What does 'hydrolysed' collagen mean?
Hydrolysed collagen means it has been broken down into much smaller peptides using natural enzymes This is important for absorption. Collagen is a large molecule that cannot be absorbed well in its original size. Hydrolysing the collagen peptides down below 10kD like Zooki does increases the absorption up to 95%.
What is collagen?
Collagen is the main protein providing the scaffolding and glue for tendons, bones, ligaments and skin. It literally keeps us upright and forms the padding for youthful, robust skin.
As we age, collagen production falls, resulting in weaker tendons and muscles as well as sagging skin and wrinkles. Maintaining collagen levels can support your strength and resilience both inside and outside the body.
Can I take collagen if I'm pregnant?
No research has been done on taking collagen whilst pregnant or breastfeeding. We advise caution and speaking to a healthcare professional before taking any new dietary supplement whilst pregnant or breastfeeding.
Is collagen suitable for vegans/vegetarians?
All collagen is derived from animal sources, so it won’t suit vegans. Vegetarians may find eggshell collagen supplements but mostly collagen is made from either fish, beef or pork.
What is collagen made from?
Collagen protein is made from amino acid building blocks but needs several co-factors such as vitamin C, zinc, manganese and copper to activate the enzymes that complete the process.
It’s not possible to absorb collagen whole as it is too big a molecule. Instead, we break collagen down into natural and bioavailable peptides that can be absorbed easily through the gut wall.
What's the difference between 5,000mg and 11,000mg Super Strength Collagen?
Both options contain the same premium, hydrolysed marine liquid collagen peptides - the only difference is the the strength per sachet and the flavours you can opt for.
What is 'hydrolysed' collagen?
Collagen in its natural state is a large chain of individual peptides that is impossible for the body to absorb. In order to help your body absorb the collagen, we 'hydrolyse' into smaller molecules that are smaller and easier for your body to absorb!
Shop Zooki Collagen
Super Strength Collagen, 11,000mg

Meet the author...
Sarah Carolides is one of the UK's top functional medicine and nutrition specialists with over 20 years experience, listed by Vanity Fair as one of 'The A-List people to know in London.'




